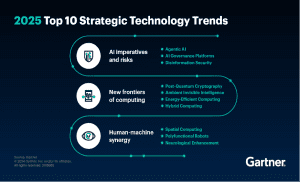
Each year, Gartner releases its Strategic Technology Trends Report, helping businesses understand what’s on the horizon. As one of the world’s leading research firms, they analyze emerging technologies and their potential impact on organizations worldwide.
Their latest report highlights ten key trends expected to shape business and technology through 2025.
Whether you’re planning your company’s tech investments or simply want to stay informed, these insights offer a practical roadmap for what’s ahead.
Let’s look at these trends and what they could mean for businesses.
1. Agentic AI
Agentic AI refers to autonomous systems capable of planning and executing actions to achieve user-defined goals without human intervention. These AI agents can function as virtual workers, handling tasks ranging from customer service to data analysis. Gartner predicts that by 2028, at least 15% of day-to-day work decisions will be made autonomously through agentic AI, up from 0% in 2024.
Implications for Business: AI assistants that can work independently can make companies more efficient by handling basic, repetitive work. This frees up employees to work on more important planning and creative tasks. However, companies need clear rules and oversight to make sure these AI systems behave appropriately and help achieve the company’s goals.
Challenges: While AI might replace some jobs, another issue is getting AI to work with company data. For agentic AI to function optimally, it requires access to vast, high-quality datasets. Many companies keep their data scattered across different systems, making it hard for AI to use it properly. Also, companies need to convince their workers and investors that AI is safe and helpful. Many people worry that AI might invade their privacy or cause problems, so building trust is important.
Actionable Steps:
- Conduct a data readiness audit to ensure data is accessible and clean.
- Launch internal communication campaigns to educate employees about AI’s benefits.
- Start with pilot projects to demonstrate AI’s value and refine its deployment before scaling.
2. AI Governance Platforms
As AI systems become more integral to business operations, governing their use is paramount. AI governance platforms provide tools to manage the legal, ethical, and operational aspects of AI deployment. These platforms help organizations create, enforce, and monitor policies that ensure responsible AI usage.
Implications for Business: Implementing AI governance platforms can mitigate risks associated with AI, such as bias and non-compliance with regulations. By ensuring transparency and accountability, businesses can build trust with employees and customers and avoid potential legal pitfalls.
Challenges: Setting up these management systems can take a lot of time and money. It’s especially hard for companies working in different countries since each place has its own rules about AI. It can also be tricky to figure out who’s responsible when AI makes mistakes.
Actionable Steps:
- Create a team of experts from different departments (legal, tech, and business) to oversee AI use.
- Buy special software that helps follow AI rules in different countries.
- Keep checking and updating AI policies to match new laws and ethical guidelines.

3. Disinformation Security
The rise of digital communication has amplified the spread of misinformation, posing significant risks to businesses. Disinformation security involves technologies and strategies designed to detect and counteract false information, protecting business integrity and reputation.
Implications for Business: Investing in disinformation security measures can safeguard a company’s brand and maintain stakeholder trust. Proactively addressing misinformation can prevent financial losses and preserve customer loyalty.
Challenges: Combating misinformation is an ongoing battle. Cybercriminals often adapt quickly, creating increasingly sophisticated false narratives. Additionally, the speed at which misinformation spreads online makes it difficult to contain.
Actionable Steps:
- Use AI-driven monitoring tools to track mentions of your brand or products across digital platforms.
- Partner with social media platforms to flag and remove harmful content quickly.
- Educate employees and customers on recognizing and reporting misinformation.
4. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
Quantum computing promises unprecedented computational power, but it also threatens current cryptographic standards. Post-quantum cryptography involves developing encryption methods resistant to quantum attacks, ensuring data security in a post-quantum world.
Implications for Business: Organizations should begin assessing their cryptographic infrastructure and plan for transitions to PQC to protect sensitive information against future quantum threats. Early adoption can provide a competitive advantage in data security.
Challenges: Transitioning to PQC can be disruptive, especially for organizations with legacy systems. Compatibility issues and a lack of skilled professionals knowledgeable in quantum-safe algorithms may delay adoption.
Actionable Steps:
- Partner with a cybersecurity firm specializing in quantum computing to bridge the skills gap.
- Develop a phased transition plan, starting with non-critical systems to minimize disruption.
- Regularly test new cryptographic solutions for performance and security to ensure readiness.
5. Energy-Efficient Computing
With increasing environmental concerns and rising energy costs, energy-efficient computing focuses on reducing the power consumption of IT systems without compromising performance.
Implications for Business: Adopting energy-efficient technologies can lower operational costs and support sustainability initiatives. This approach not only benefits the environment but also appeals to eco-conscious consumers and investors.
Challenges: Organizations may struggle with justifying the upfront investment required for energy-efficient systems, particularly in tight-budget environments. There’s also the challenge of choosing the right technologies among many competing solutions.
Actionable Steps:
- Perform an energy audit of your IT infrastructure to identify areas with the highest inefficiencies.
- Explore financing options such as green loans to support eco-friendly technology upgrades.
- Partner with vendors that have established sustainability practices and proven results.

6. Hybrid Computing
Hybrid computing combines various computing paradigms, such as cloud, edge, and on-premises systems, to optimize performance and flexibility. This approach allows businesses to leverage the strengths of different environments to meet diverse operational needs.
Implications for Business: Implementing hybrid computing can improve scalability and resilience. Organizations can process data closer to its source for real-time insights while taking advantage of cloud resources for broader analytics, leading to more informed decision-making.
Challenges: Seamlessly integrating different computing environments can lead to performance bottlenecks and security vulnerabilities. Organizations may also face challenges in upskilling their IT teams to manage hybrid systems.
Actionable Steps:
- Create a hybrid computing strategy that clearly defines workloads best suited for cloud, edge, or on-premises environments.
- Conduct regular security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Invest in training programs for IT staff to build expertise in hybrid architecture.
7. Spatial Computing
Spatial computing integrates digital and physical environments using technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). This fusion creates immersive experiences that can transform how businesses interact with customers and conduct operations.
Implications for Business: Spatial computing can revolutionize product design, training, and customer engagement. For instance, virtual showrooms can enrich the shopping experience, and AR-based training can improve employee skill development.
Challenges: The immersive nature of spatial computing requires significant computational resources and cutting-edge hardware, which may be cost-prohibitive for smaller organizations. User adoption can also be slow if the applications are not intuitive.
Actionable Steps:
- Start with simple, scalable projects like AR apps for product visualization before moving to more complex VR setups.
- Collaborate with academic institutions or innovation hubs to experiment with spatial computing at lower costs.
- Gather user feedback early to ensure solutions meet customer or employee needs.
8. Polyfunctional Robots
Unlike traditional robots designed for specific tasks, polyfunctional robots are versatile machines capable of performing multiple functions. They can adapt to different roles, making them valuable assets in dynamic business environments.
Implications for Business: Deploying polyfunctional robots can increase flexibility and efficiency. In manufacturing, for example, a single robot could handle assembly, quality control, and packaging, reducing the need for multiple specialized machines.
Challenges: High initial costs and the complexity of integrating robots into existing workflows are significant hurdles. Additionally, resistance from employees who fear job loss or prefer traditional methods can impede adoption.
Actionable Steps:
- Begin with automation in areas where it can have the most immediate impact, such as repetitive tasks.
- Run training programs to upskill employees, showing them how to work alongside robots rather than be replaced by them.
- Work with robotics companies who provide ongoing support and maintenance.

9. Neurological Enhancement
Advancements in technology are enabling enhancements to human cognitive abilities through interfaces that interact directly with the brain. These developments have the potential to improve productivity and innovation.
Implications for Business: Adopting affordable cognitive tools can improve employee efficiency, reduce burnout, and foster innovation. These technologies are easy to implement and offer immediate benefits without significant investments.
Challenges: Businesses may face challenges in determining which tools offer real value versus those that are simply trendy. Additionally, privacy concerns may arise if tools collect data on employee performance or mental health.
Actionable Steps:
- Evaluate Affordable Tools: Start with free or low-cost solutions, such as apps designed to boost focus (e.g., time-blocking software) or improve memory retention.
- Prioritize Privacy: Choose tools that prioritize employee privacy and comply with data protection regulations.
- Employee Buy-In: Introduce these tools as part of wellness initiatives to encourage voluntary adoption and avoid concerns about surveillance.
- Measure ROI: Track improvements in productivity or employee satisfaction to assess the impact of these initiatives.
10. Ambient Invisible Intelligence
This trend involves putting smart technology into everyday spaces – like rooms, buildings, and objects – so they can understand what people need without being noticed. Think of sensors and internet-connected devices that work quietly behind the scenes, like lights that automatically adjust when you enter a room or thermostats that learn your temperature preferences.
Implications for Business: Smart technology that works quietly in the background can make things better for customers and help businesses run smoother. For instance, stores can customize each shopper’s experience, and smart buildings can save money by using less energy.
Challenges: Ensuring that ambient systems are secure and don’t breach privacy laws is a major concern. Additionally, businesses may face challenges in demonstrating ROI for technologies that operate seamlessly in the background.
Actionable Steps:
- Conduct privacy impact assessments for all ambient intelligence solutions.
- Educate users on how these systems work and the safeguards in place to protect their data.
- Use pilot programs to measure tangible outcomes, such as increased customer engagement or reduced energy consumption.
Making Technology Trends Work for Your Business
As businesses navigate the evolving tech landscape through 2025, Gartner’s insights provide valuable guidance for strategic planning. While not every trend will make sense for every organization, understanding these developments helps companies make informed decisions about where to invest their resources.
The key is to evaluate which of these technologies align with your business goals and could offer practical benefits to your organization. This selective strategy helps ensure technology investments deliver measurable value and long-term results.
About Atlantic, Tomorrow’s Office
Atlantic is an award-winning office technology and IT solutions company providing Imaging Products, IT Support, Document Management, Cybersecurity and Managed Services to small and large companies in the New York City metropolitan area, and the Greater Philadelphia and Delaware Valley.
For the latest industry trends and technology insights visit ATO’s main Blog page.